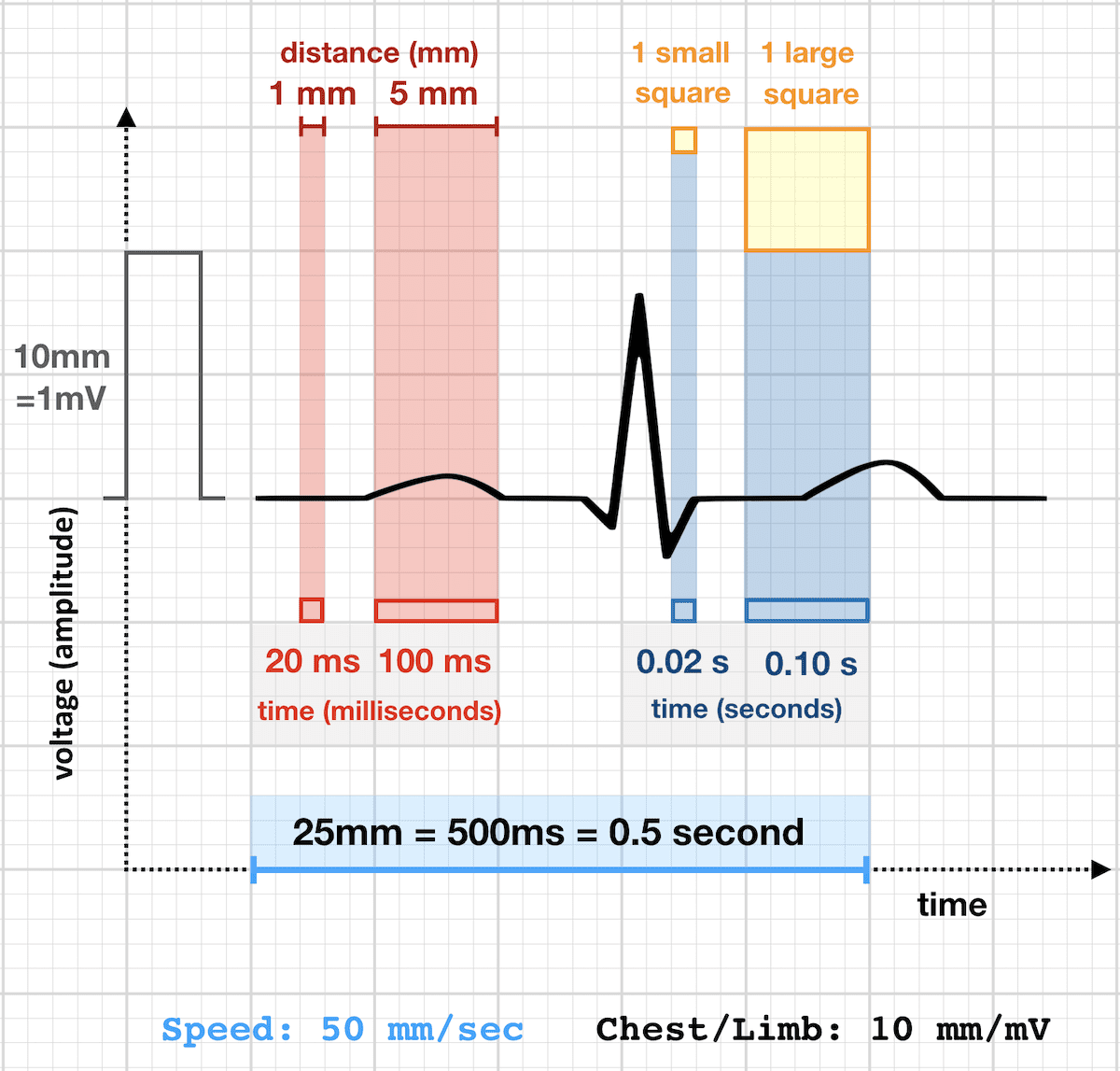
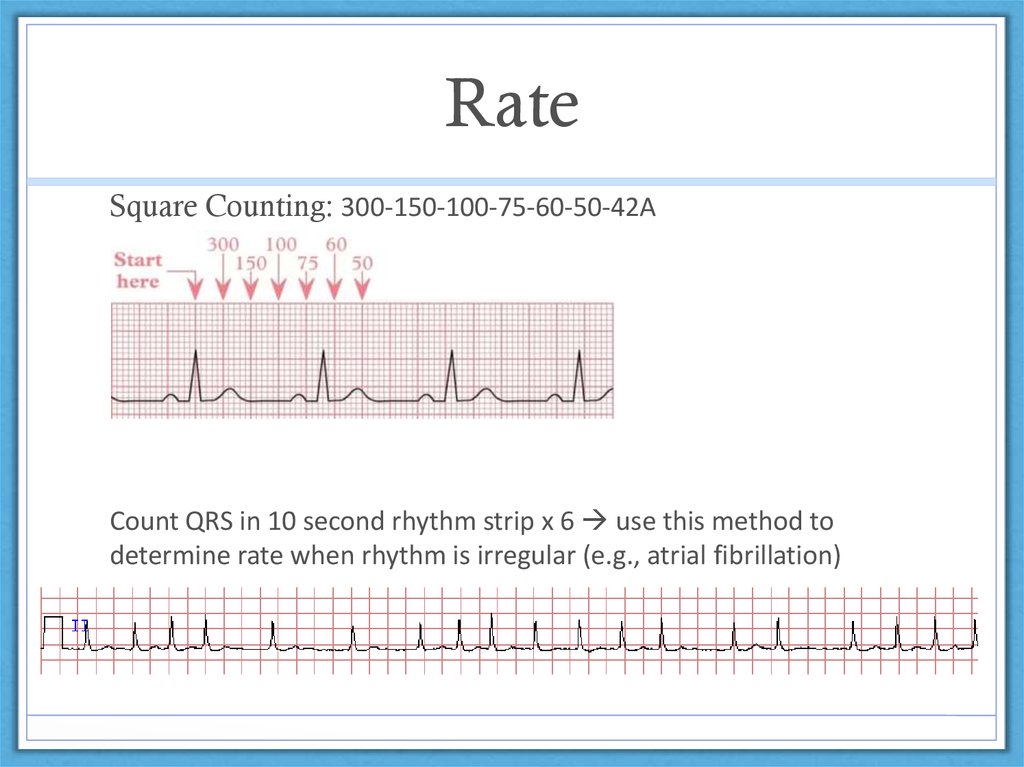
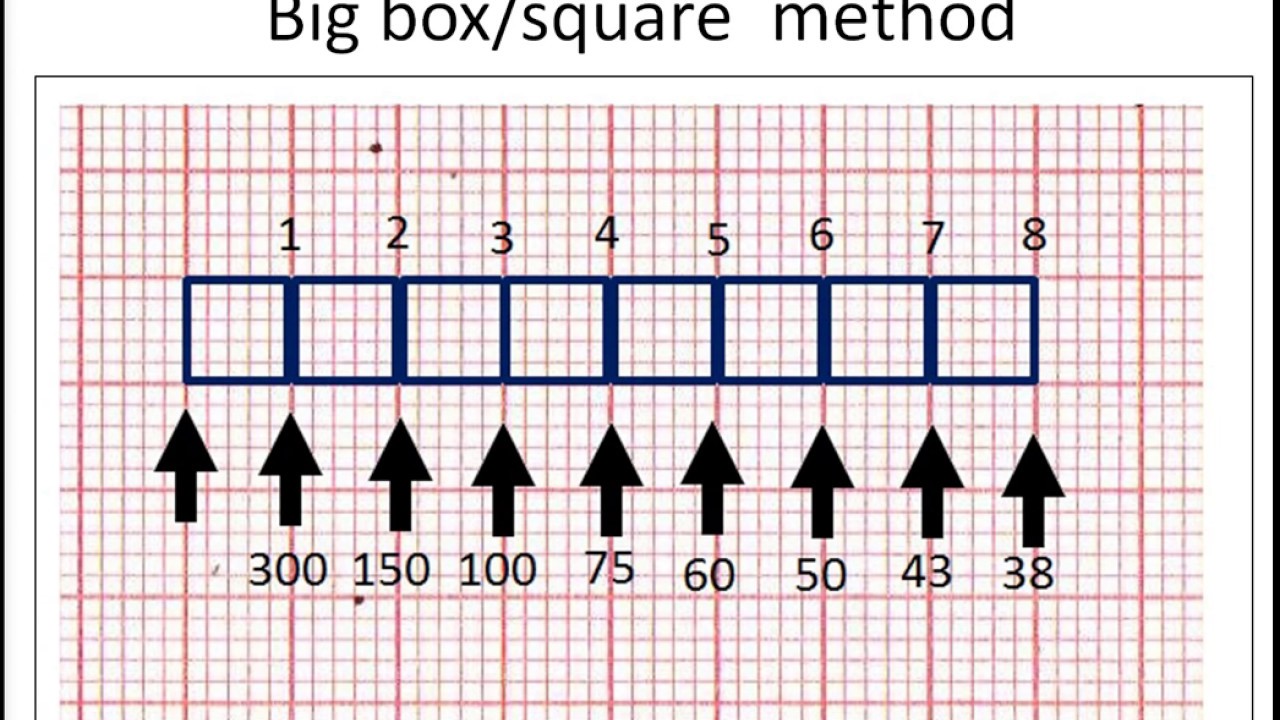
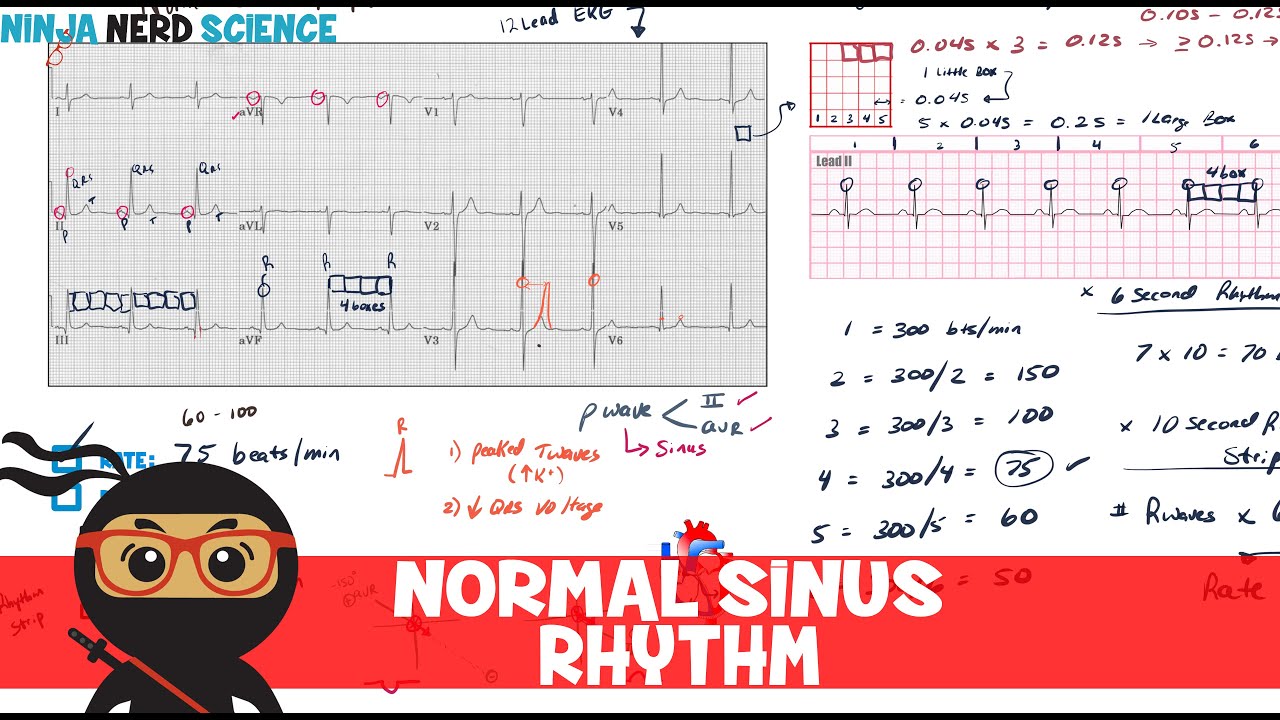
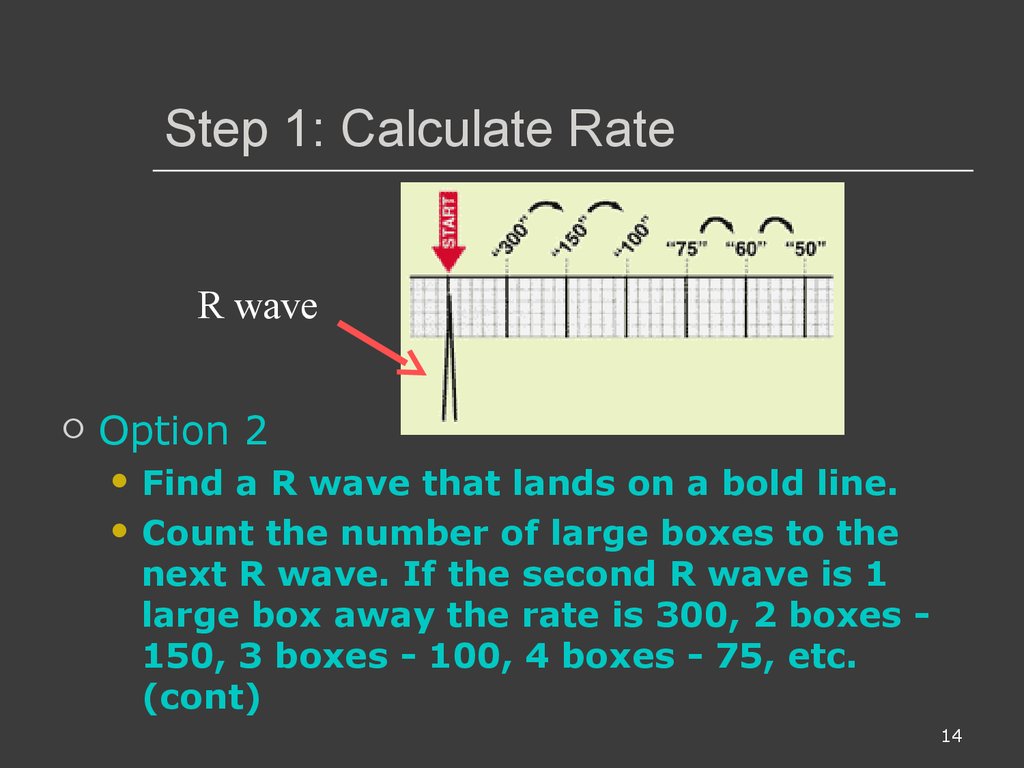
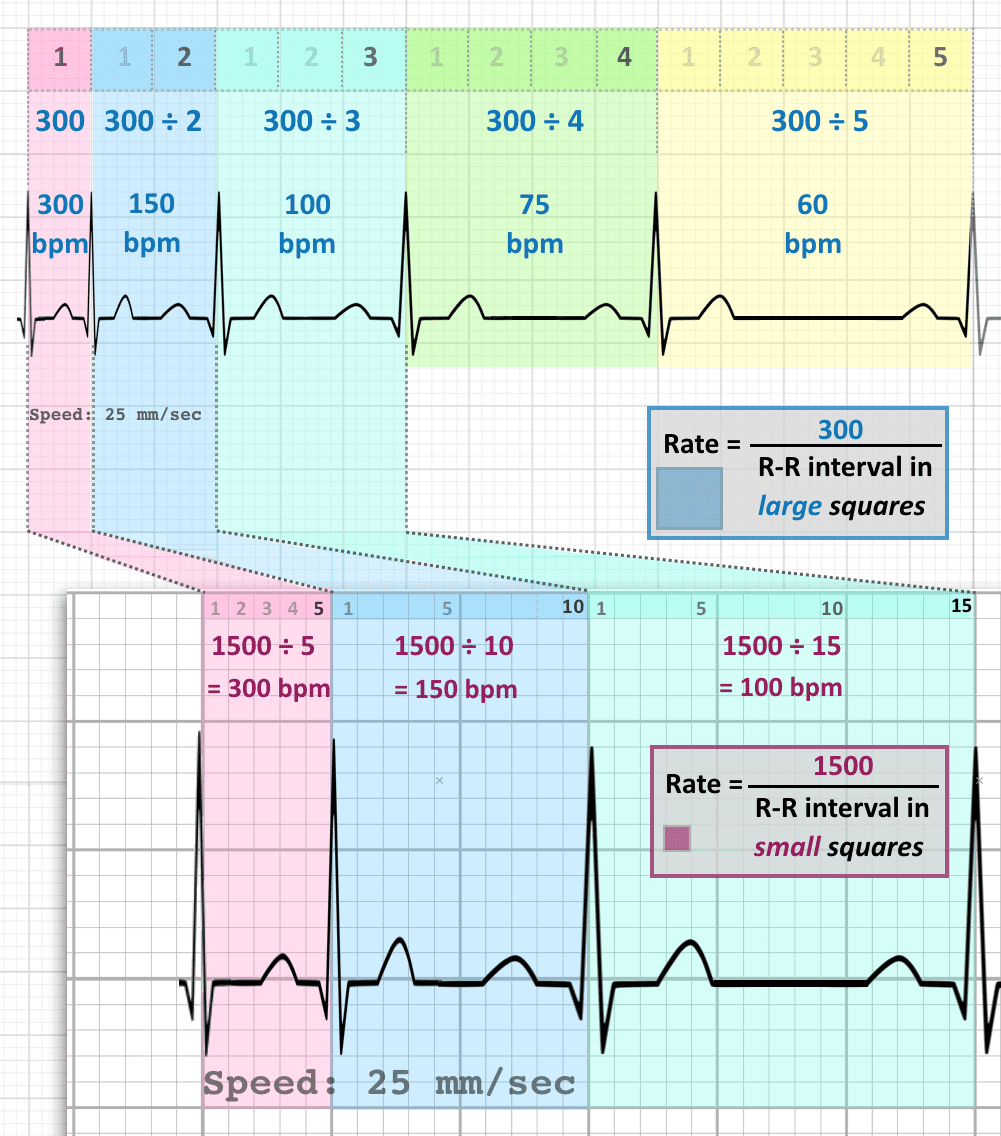
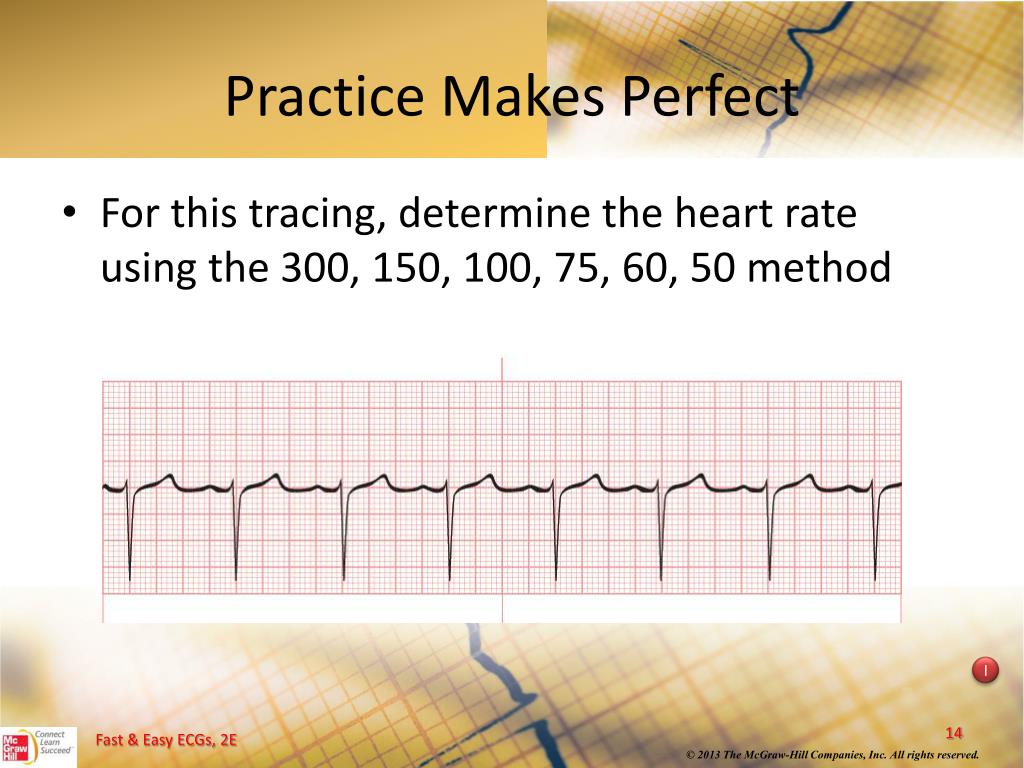
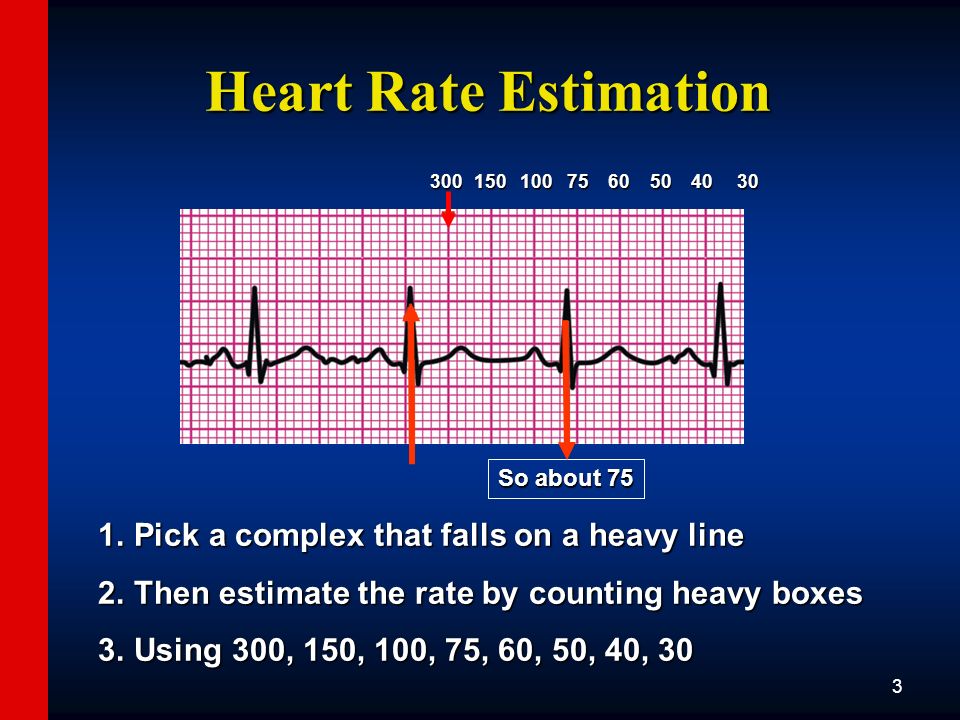
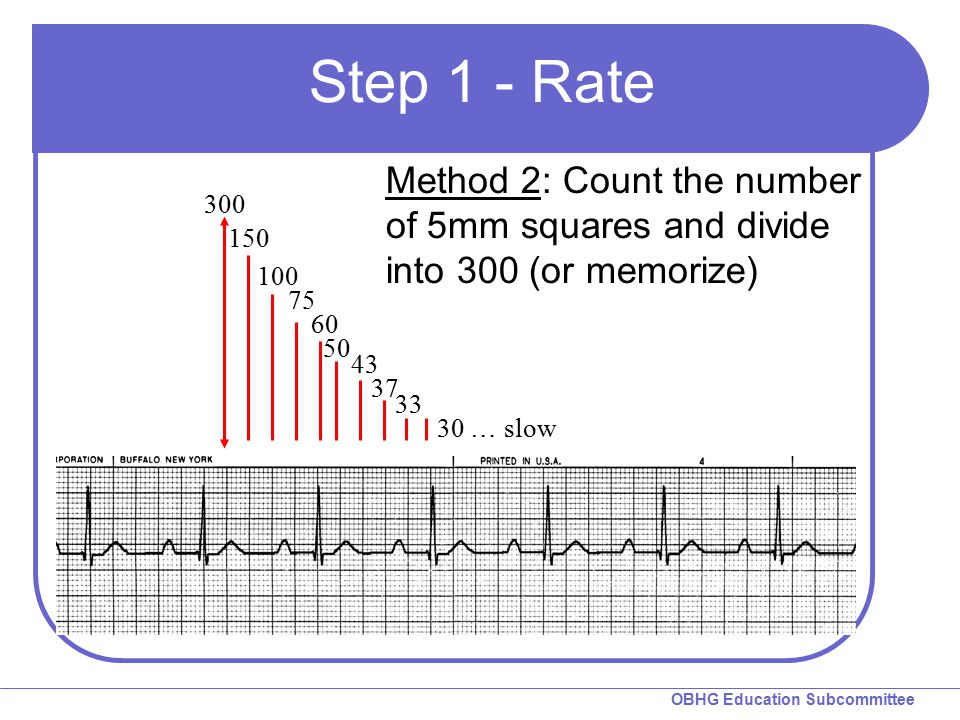
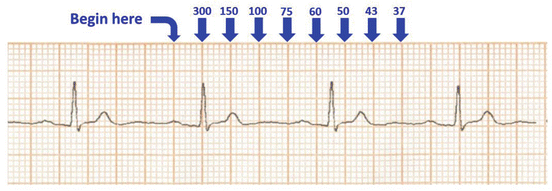
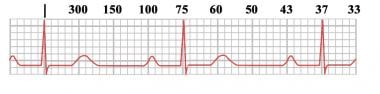
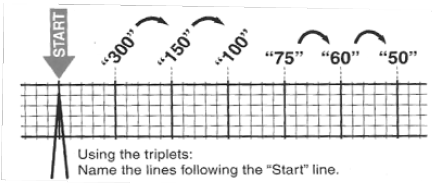
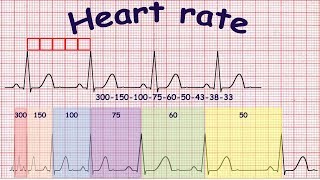
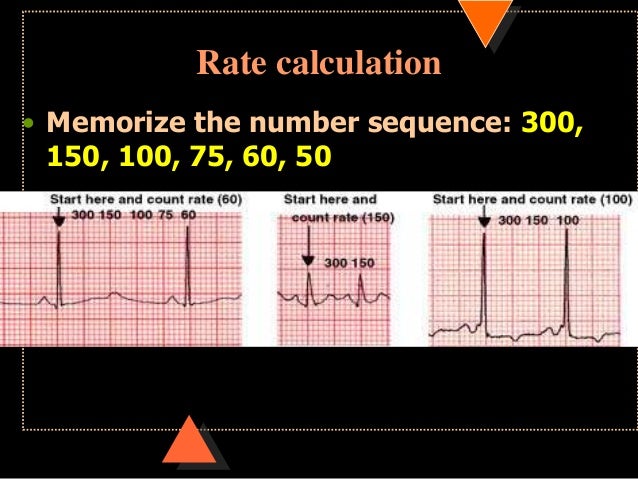
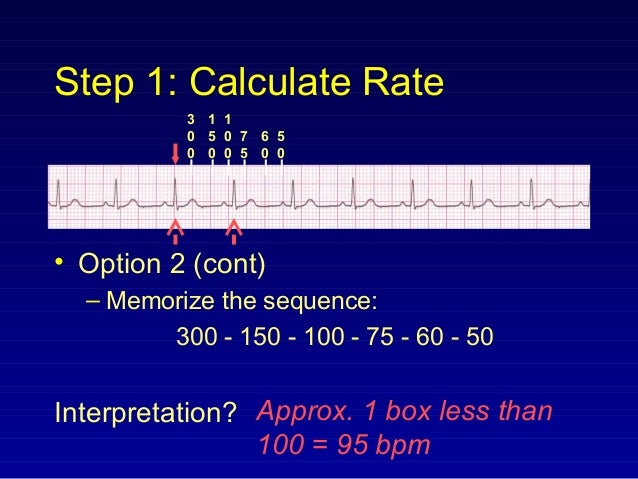
300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50, 43, 37, 33 The heart rate irregular rhythm If the heart rate is irregular, count the number of QRS complexes on the ECG and multiply by 6 to obtain the average heart rate The ECG paper will show a period of 10 seconds Therefore 6300/1 = 300 per minute 2 large squares 300/2 = 150 per minute 3 large squares 300/3 = 100 per minute 4 large squares 300/4 = 75 per minute 5 large squares 300/5 = 60 per minute 6 large squares 300/6 = 50 per minuteSi son regulares podremos usar la regla de los 300 para calcular la frecuencia cardíaca (dividir 300 por el nº de lineas gruesas que hay entre un QRS y el siguiente QRS, ) 2) ONDA P debe de estar presente, y debe estar seguida de un QRS Será positiva en II y negativa en aVR Alcanza su mayor voltaje en II
Ecg Rate Interpretation Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Basics
Ecg 300 150 100 75 rule
Ecg 300 150 100 75 rule-The mnemonic "" to estimate the rate in beats per minute (BPM) In other words if you pass 2 lines before the next QRS, the heart rate (HR) would be less than 150 Remember that this is merely an estimate You should useFrom Rapid Interpretation of EKG's by Dale Dubin, MD COVER Publishing Co, PO Box , Fort Myers, FL , USA Personal Quick Reference Sheets Dubin's Method for Reading EKG's 1 RATE (pages 6596) Say "300, 150, 100" "75, 60, 50" • but for bradycardia rate = cycles/6 sec strip 10 2 RHYTHM (pages 972)




How To Read An Ecg Physical Therapy Reviewer
Cuente "300, 150, 100" para las tres líneas gruesas que le siguen a la línea inicial y consecutivamente para las que le siguen a las primeras tres iniciales Donde la siguiente onda R cae, eso determina la frecuencia Heart rates associated with each of the large boxes in the following order are 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50, 43, 37, 33 beats per minute (bpm) View Media Gallery Heart rate boxes300 150 ekg • 300 method – 300, 150, 100, 75, 60 Rate • 10 second method • Each EKG is 10 seconds • Count total QRS complexes • Multiply by 6 Rate • Normal 60 – 100 • Bradycardia < 60 • Tachycardia > 100 Rhythm • Sinus •Atrial • Supraventricular • Junctional • Ventricular
All you do is find an Rwave that is lined up with a large block on the ECG paper and count the number of large blocks between that cardiac cycle and the next In other words, you measure the RR interval in large blocks 6 large blocks 50;1 large block 300Facile e comprensibile lettura di un ecg, elettrocardiogramma, derivazioni periferiche, D1, D2, D3, aVF, aVL, aVR, comprendere le aritmie, se essa cade sulla prima linea in neretto= 300 di frequenza, altrimenti 150, 100, 75 60, 50, come si vede nell'esempio in schema;
The Cardiac Ruler or Sequence Method Count the number of big boxes between R waves and count using the following numbers This can only be used on regular rhythms and not on irregular rhythms1) Lo primero que vamos a hacer es buscar una onda R que coincida con una línea negra gruesa en el ECG Si hubiese otra onda R en la línea gruesa que le sigue a la onda R que ubicamos la frecuencia sería de 300 lpm (es decir a 5 cuadraditos chicos o uno grande), si estuviese a dos líneas gruesas sería de 150, a tres de 100, a cuatro de 75, a cinco de 60, a seis de 50RATE 300 150 100 75 60 50 43 LVH RVH LAE RAE AXIS DEVIATION Normal Left Right Lead I QRS Lead II/aVF QRS Q WAVES • Can be normal in leads aVL, I, II, V5, V6 • Can be normal on expiration in lead III PATHOLOGICAL Q WAVES • > 2 small squares deep • >25% of height of following R wave in depth • >1 small square wide ST SEGMENT ELEVATION • (New STE at the J



Ecg For Interns Online Presentation



Co Grand Co Us Documentcenter View 636 Heart Rate Fast And Easy Ecgs Shade Wesley
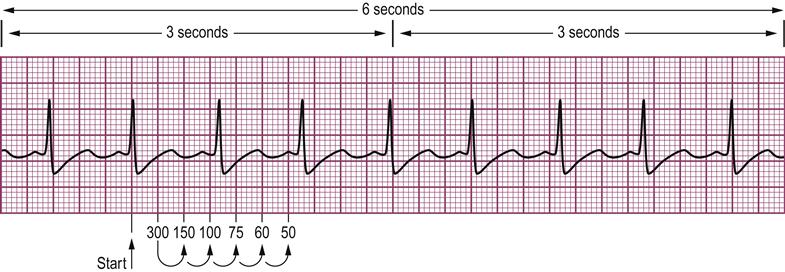
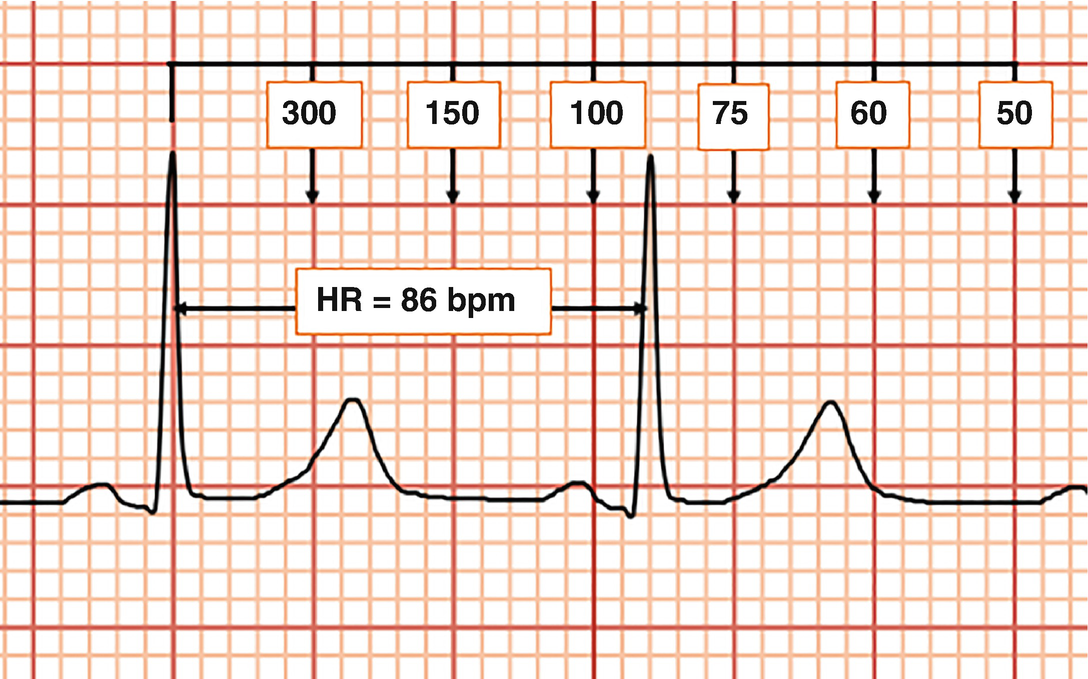
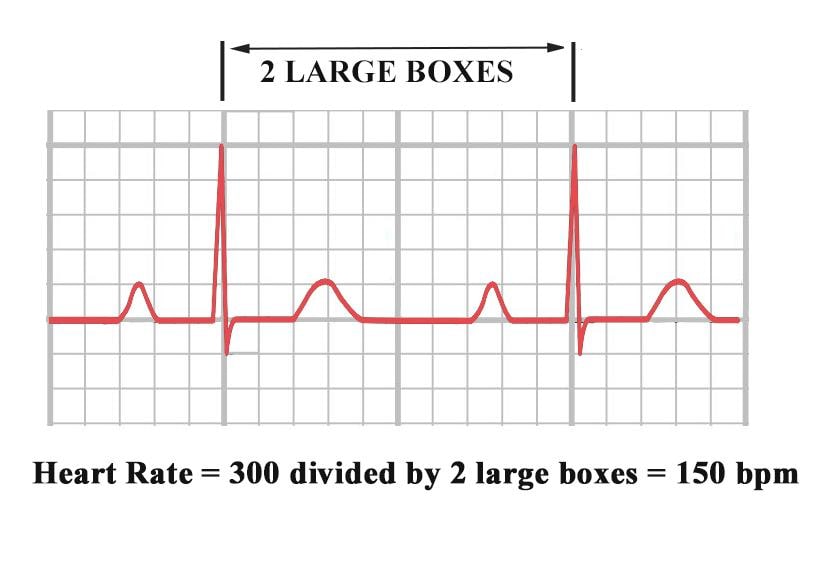
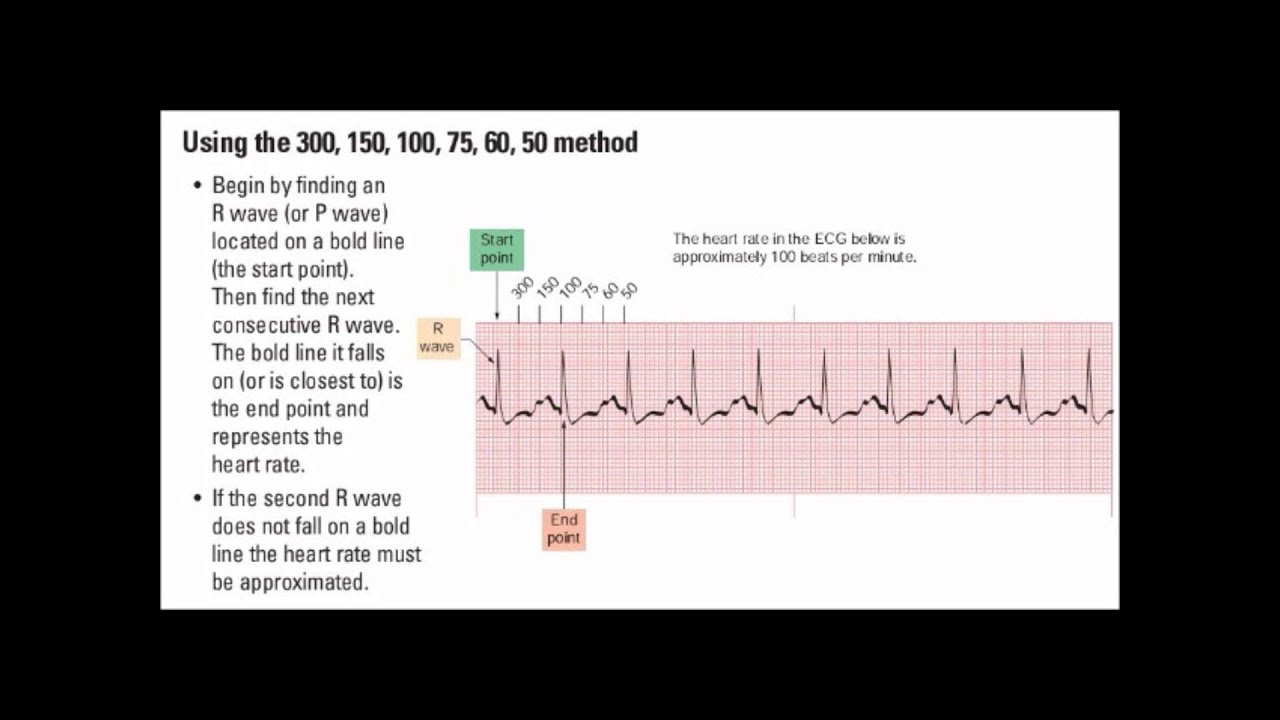
2 large blocks 150;3 large blocks 100;Rate, rhythm and axis from an ECG 1)Rate The ECG paper runs at 25 mm/sec through the ECG printer Use the sequence Count from the first QRS complex, the first thick line is 300 bpm, the next thick line 150 etc Stop the sequence at the next QRS complex



How To Compute The Rate Youtube



Rate And Rhythm Normal Sinus Rhythm Youtube
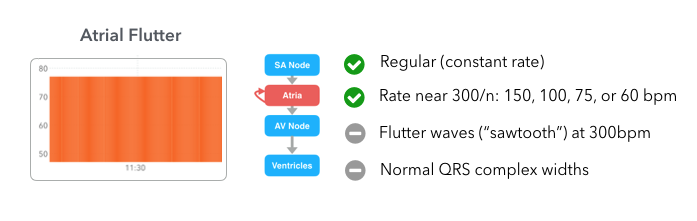
ECG Paper Systematic Approach to Reading an ECG Lead Placement Hexaxial System •300 big boxes = 60 sec •Rate = 300/# big boxes 300 150 100 75 60 50 The RateSawtooth F waves visible at rate of ~300 Usually ~150 or ~75 (21 and 41 conduction of atrial impulses respectively) Regular Atrial fibrillation No P waves, The Rule of 300 when the rhythm is regular = 300 / (number of boxes between R to R wave) Six Second300 150 ecg rule Wwwk300org is the online home of the Kuskokwim 300, the world's premier middle distance sled dog race "From Bethel, Alaska to Aniak, and back!" Heart rates associated with each of the large boxes in the following order are 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50, 43, 37, 33 beats per minute (bpm) View Media Gallery Heart rate boxes




Learntheheart Com Determining Hr On Ecg Based On Of Big Boxes Between Qrs Complexes 1 300 2 150 3 100 4 75 5 60 6 50 Http T Co Sjfwimitat



1
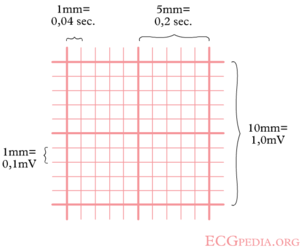
5 large blocks 60;How to read an EKG • The paper – Up and down 1 box = 01 mV –Across 1 box = 4 ms • The rate – 10 seconds per page Él que más utilizo es el de y si os fijais bien estos números se sacan de dividir 1500 entre el número de cuadraditos pequeños Por ejemplo 1500/5=300, 1500/10=150, 1500/15=100, 1500/=75, etc Aunque tb uso el de contar el nº de ciclos en un intervalo de 6 segundos x 10




Patwari Academy Ecg Rate Rhythm Axis



Co Grand Co Us Documentcenter View 636 Heart Rate Fast And Easy Ecgs Shade Wesley
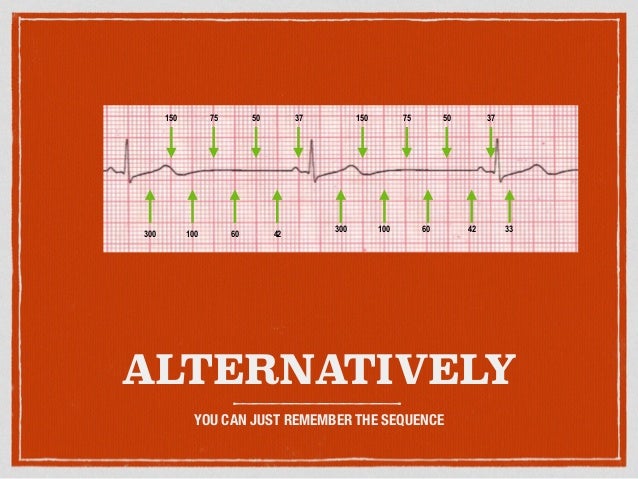
Cette méthode utilise une série de chiffres 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50, 43, 38, 33, 30 Chacun des chiffres correspond à la fréquence équivalente à une augmentation de 1 carré, sur 1 minute Puisque un grand carré correspond à 0,2 seconde, il est alors facile d'estimer la fréquence cardiaque en comptant les carrés300 150 100 75 60 50 43 LVH RVH LAE RAE AXIS DEVIATION Normal Left Right Lead I QRS Lead II/aVF QRS Q WAVES • Can be normal in leads aVL, I, II, V5, V6 • Can be normal on expiration in lead III PATHOLOGICAL Q WAVES • > 2 small squares deep • >25% of height of following R wave in depthSe ce ne sono due, 150 bpm;



The Basics Of Ecg Acls Medical Training



Large Block Method To Calculate Heart Rate Ecg Medical Training
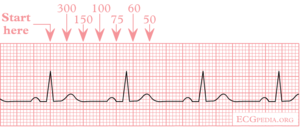
De aftelmethode (het liefst te gebruiken bij een normaal sinusritme) Hierbij gebruikt men de sequentie Men begint met aftellen bij een willekeurige Rgolf (liefst een die toevallig op een dikke lijn valt) Dit is het startpuntDe 300 Con esto deducimos que si el intervalo RR es de 5 mm la frecuencia cardíaca es de 300 lpm Si hacemos lo mismo con 10 mm obtendremos 150 y así sucesivamente iremos obteniendo múltiplos de 300, de manera que seremos capaces de saber inmediatamente la frecuencia cardíaca si memorizamos las siguientes cifras 300, 150, 100, 75, 60 ,50For example if there is 1 large square between R waves, the heart rate is 300 bpm;




How To Find Heart Rate Pulse From Ekg Youtube




How To Read An Ecg Physical Therapy Reviewer
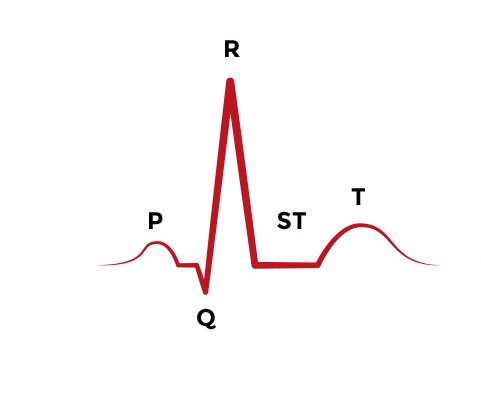
Two large squares, 150 bpm, three large squares, 100 bpm, four 75 bpm What if the Second R Wave Does Not300, el número mágico de la frecuencia cardiaca En un electrocardiograma normal por cada segundo hay cinco cuadros grandes, por tanto en un minuto hay 300 cuadros grandes (ver características del papel de EKG) Sabiendo esto, podemos calcular la frecuencia cardiaca midiendo el intervalo RR, siempre que el ritmo sea regularECG Basics 3, Use the sequence P waves absent;



Large Block Method To Calculate Heart Rate Ecg Medical Training



2
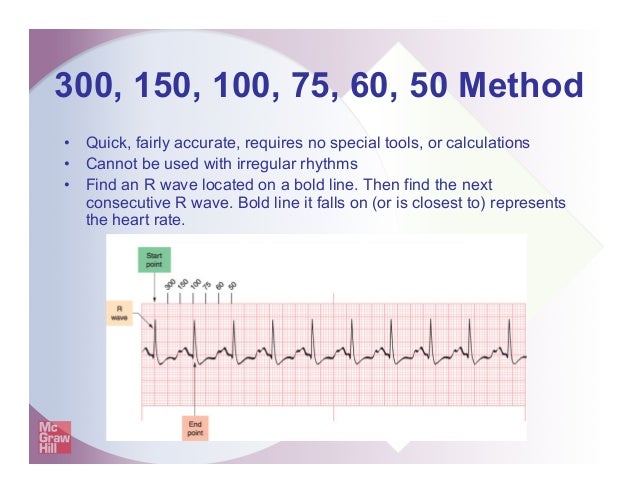
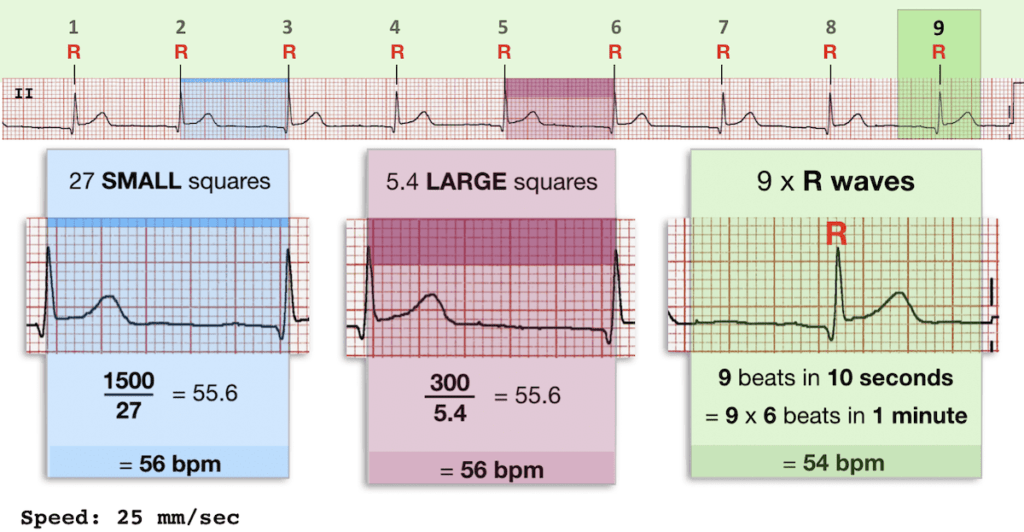
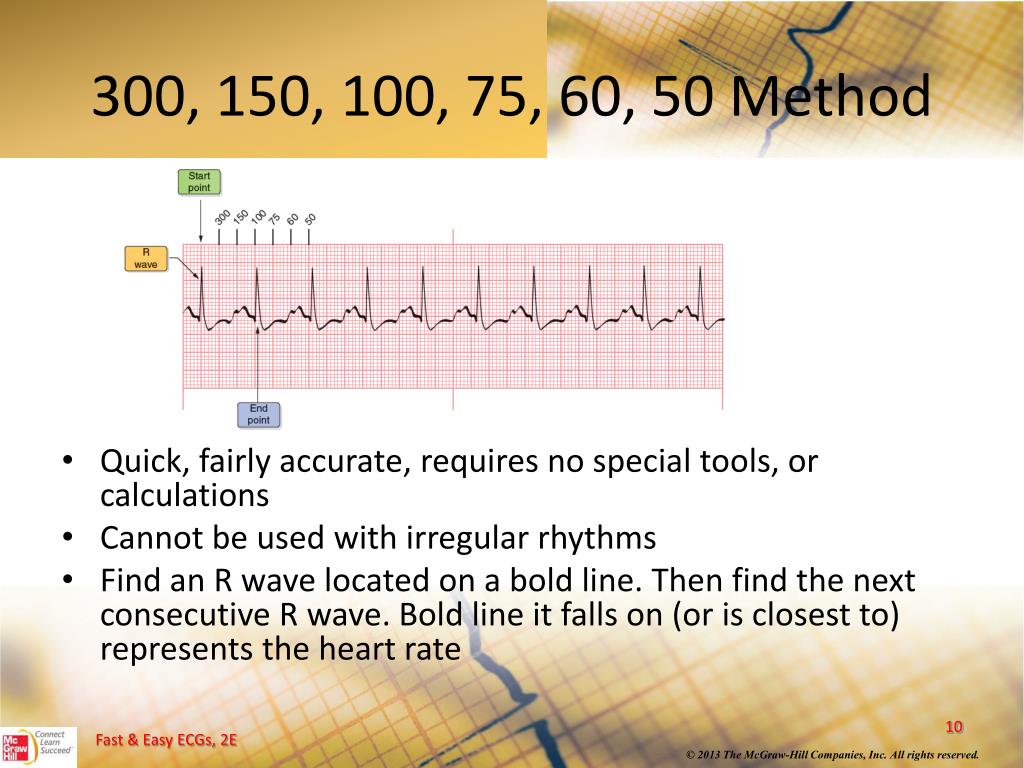
Interpretation of ECG Rhythm Normal Sinus Rhythm Rate b/min Rhythm regular P waves upright in leads I, II, aVF PR interval < s QRS < 10 s Sinus Bradycardia Rate < 60 bpm Rhythm regular Sinus Tachycardia Rate > 100 bpm AV Conduction Disturbances Atrioventricular conduction disturbances refer to blockage of electrical impulseReview some aspects of EKG that are troubling to some in the field 5 Learn from a couple of unique situations What NOT 1 A comprehensive review of all aspects of EKG Box count method large boxes 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50 Rate= Normal, 64 P for every QRS, QRS for every P Normal and consistent P's and PR's Normal Sinus Rhythm P P PQRS complexes found in a 6second portion of the ECG tracing • The 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50 method involves locating an R wave on a bold line on the ECG paper, then finding the next consecutive R wave and using the 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50 values for subsequent bold lines to determine the rate



Ecg Interpretations How To Analyze A Rhythm Normal Sinus Rhythm Heart Arrhythmias Diagnosing A Myocardial Infarction Online Presentation




Ekg Lecture Series Fundamentals Flashcards Quizlet
Place the beginning point of a cardiac ruler over an R wave Look at the number on which the next R wave falls and that becomes the heart rate for that patient Use the following numbers to indicate what the heart rate is between two successive R waves 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50, 43, 37, 33, 30 Method # 2 The Six Second Tracing MethodThe dark vertical lines correspond to 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, and 50 bpm For example, if there are three large boxes between R waves, the patient's heart rate is 100 bpm There are more accurate ways to determine heart rate from ECG, but in lifesaving scenarios, this method provides a Calcul de la FC par la méthode des 300 (Débuter le calcul de préférence à partir d'un QRS qui tombe sur un trait gras) La FC correspondant à deux QRS séparés par 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 grand(s) carreau(x) correspond à 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50, 43, 38, 30/min




Ecg




The Second Method Uses Small Boxes Count The Number Grepmed
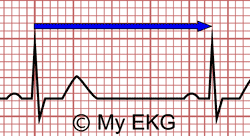
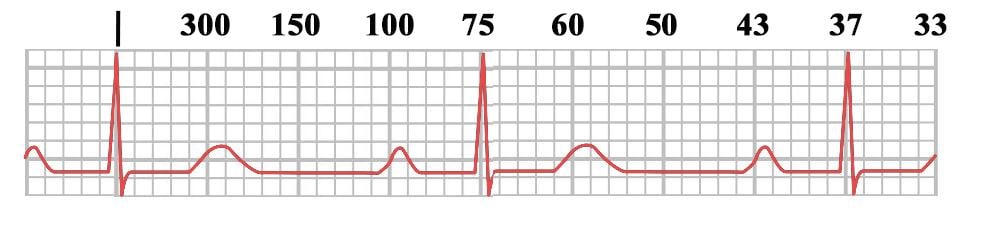
On the EKG, locate a R wave that matches a thick line, count the number of large squares to the next R wave Heart rate is 300 divided by the number of large squares , and that's it!Begin by quickly checking ECG monitor or tracing to see 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50 Method Determine the heart rate using the 6second interval x 10 method ecg_fast_and_easy_chp3pdfEcg 300 150 100 75 Use the sequence Count from the first QRS complex, the first thick line is 300, the next thick line 150 etc Stop the sequence at the next QRS complex When the second QRS complex is between two lines, take the mean of the two numbers from the sequence or use the finetuning method listed belowTwo large squares, 150 bpm, three




Electrocardiography Cardiovascular And Pulmonary Physical Therapy Second Edition An Evidence Based By William E Deturk



How To Calculate The Heart Rate On An Ekg
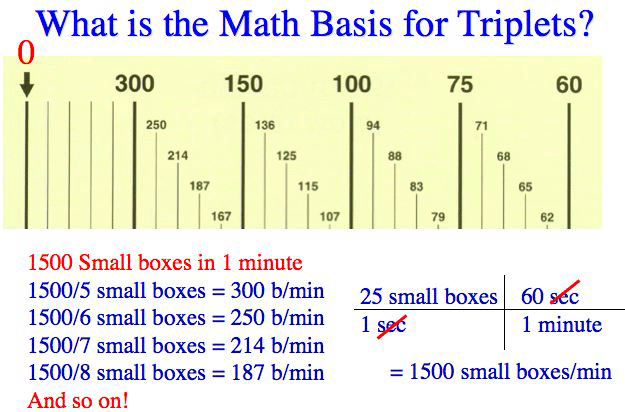
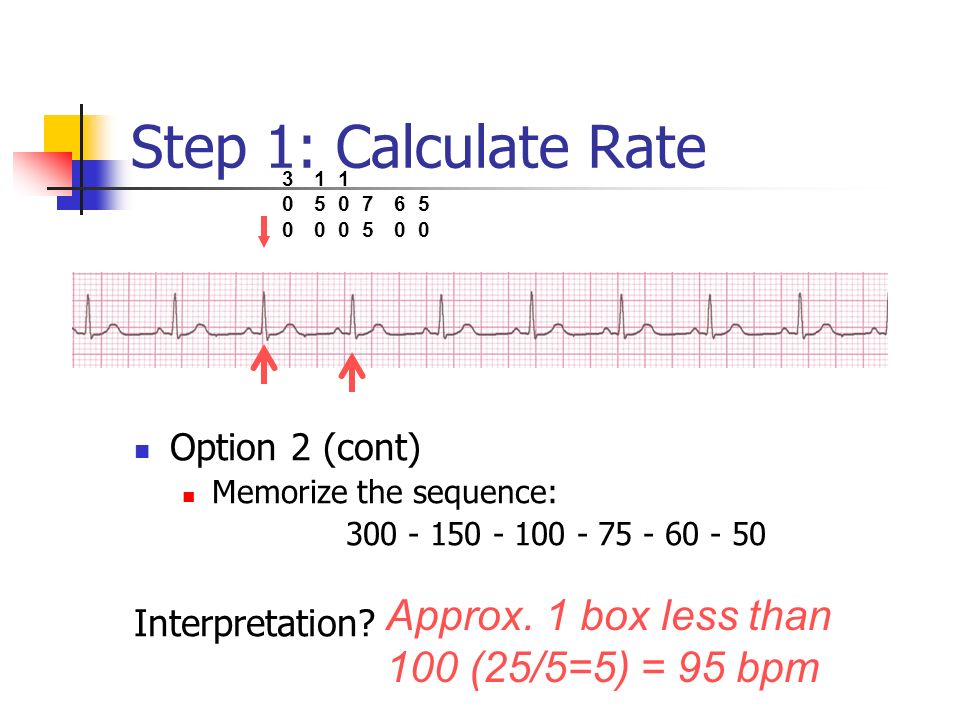
4 large blocks 75;300, 150, 100, 75, 60 50 method small boxes / 1500 method Normal ECG range 가로/세로A simple, Take the duration between two identical points of consecutive normal ECG waveforms such as the RR duration (keep units in seconds), MD COVER Publishing Co, 100, RATE (pages 6596) Say "300, And this heart rate is 150, the HR is approx, take the mean of




How To Read An Ecg Wikidoc




Medicowesome Mnemonics And Basics Of Ecg Interpretation
Use the sequence Count from the first QRS complex, the first thick line is 300, the next thick line 150 etc Stop the sequence at the next QRS complex When the second QRS complex is between two lines, take the mean of the two numbers from the sequence or use the finetuning method listed below Another method, which gives a rough approximation, is the "count off" method Simply count the number of large squares between R waves with the following rates 300 150 100 75 60 For example, if there are three large boxes between R waves, then the rate is 100 beats/min One must extrapolate, however, between boxesTwo large squares, 150 bpm, three large squares, 100 bpm, four 75 bpm



Ekg Paper Ems Education




12 Lead Ecg Placement Aed Superstore Resource Center
O método mais simples é contar o número de quadrados grandes na sequência 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50, 43, 38, 33 Voltagem no ECG A altura ou amplitude no papel de ECG representa a voltagem do estímulo elétricoRate ECGpedia Education Details Use the sequence Count from the first QRS complex, the first thick line is 300, the next thick line 150 etc Stop the sequence at the next QRS complex When the second QRS complex is between two lines, take the mean of the two numbers from the sequence or use the finetuning method listed belowFor example if there is 1 large square between R waves, the heart rate is 300 bpm;




How To Read An Ecg




Chapter 4 And 5 Review Chapter 04 Heart Rate Chapter 05 Regularity Chapter 04 Heart Rate 10 Studocu
Figura 1B – Método del 300 para calcular la FC en un EKG En la Figura 1B se muestra otro ejemplo del método del 300 para calcular la Frecuencia Cardíaca en un Electrocardiograma En este ejemplo hay 3 cuadros grandes entre ambas Ondas R por lo que la Frecuencia es de 100 lpm (300/3 = 100)300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50 method involves locating an R wave on a bold line on the ECG paper this is referred to as the "start point" each bold line to the right of the "start point" has a values that denotes the heart rate the first bold line is Este método es el más sencillo y rápido Se elige una onda R que caiga cerca de una línea gruesa del papel de EKG La primera línea gruesa a la derecha corresponde a 300, la segunda a 150, la tercera 100, la cuarta a 75



Ecg Rate Interpretation Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Basics



Co Grand Co Us Documentcenter View 636 Heart Rate Fast And Easy Ecgs Shade Wesley
Individuiamo nell'ECG un'onda R che coincide con una linea spessa, contiamo il numero di quadrati che ci sono fino all'onda R successiva e dividiamo 300 per il numero di quadrati grandi Esempio se esiste un quadrato tra due onde R, 300 bpm;How to Calculate the Heart Rate on an EKG › Top Education From wwwmyekgcom Education Details Heart rate is 300 divided by the number of large squares, and that's it!Use the sequence Count from the first QRS complex, the first thick line is 300, the next thick line 150 etc Stop the sequence at the next QRS complex When the second QRS complex is between two lines, take the mean of the two numbers from the sequence




Arrhythmetics And The Magic Numbers In Cardiology Thoracic Key




Calculate Heart Rate From Ecg Heart Rate Heart Phlebotomy
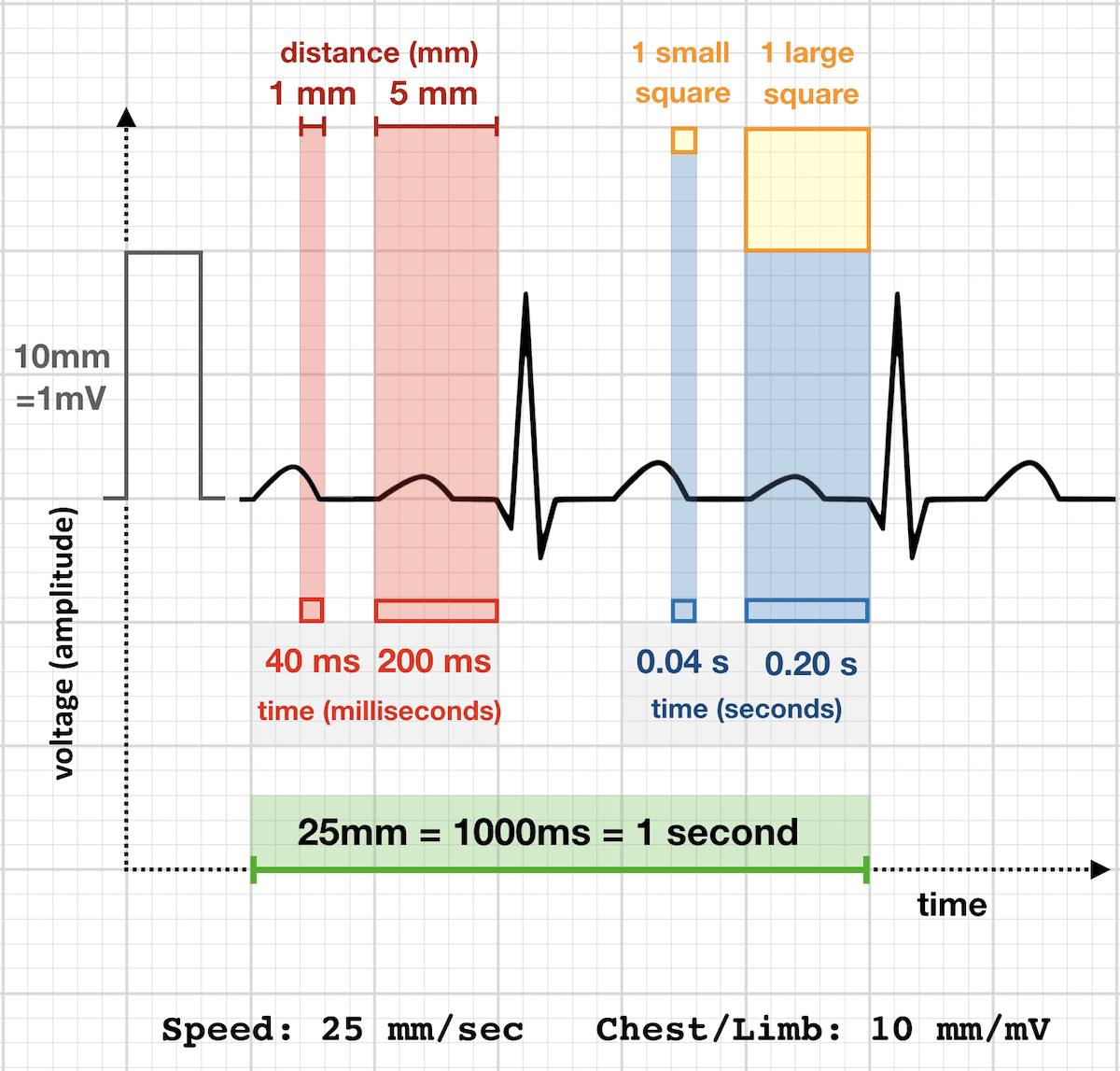
Ecg paper • • 0 300 150 100 75 60 50 42 bpm 25mm/sec 004 sec 02 sec 1 sec



Ppt Heart Rate Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Cardiac Arrhythmias And Conduction Disturbances Musculoskeletal Key




Ecg Interpretation Interactive Case Studies Pages 1 42 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5




Ecg Rate Interpretation Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Basics



Centegra Org Wp Content Uploads Bradycardia 7 Pdf




Introduction To Ecg Interpretation Electrocardiogram Interpretation Is An



How To Calculate The Heart Rate On An Ekg




Rate



How To Calculate Heart Rate From



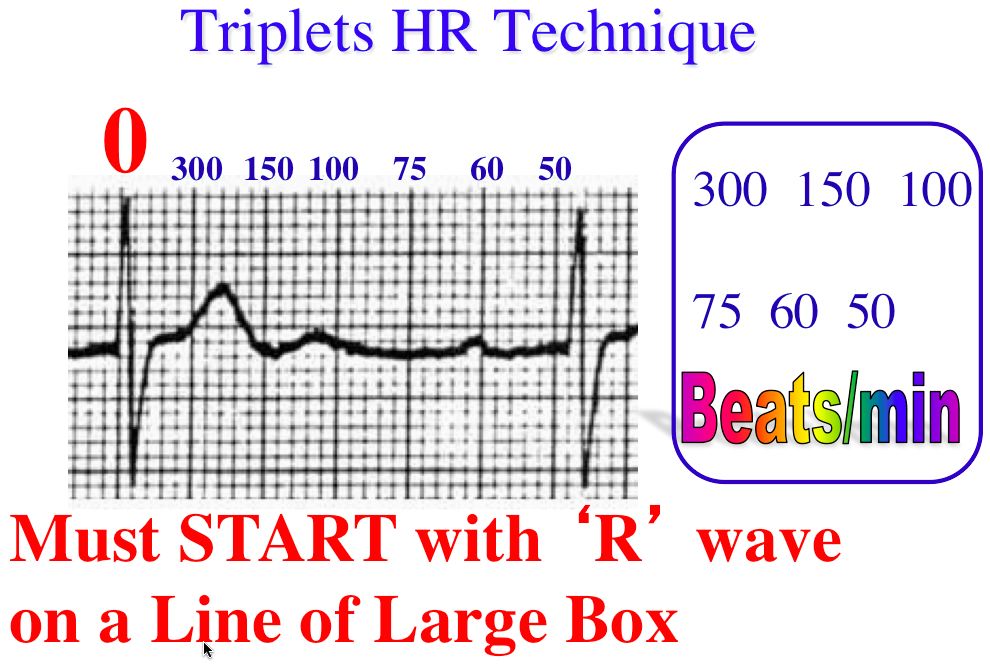
Triplets R To R 6 Second Heart Rate Method



Large Block Method To Calculate Heart Rate Ecg Medical Training




Dentistry And Medicine Ecg Rhythm Interpretation How To Analyze A Rhythm



Http Www Thaiheart Org Images Column asic Ecg Part1 1 Pdf



1



Co Grand Co Us Documentcenter View 636 Heart Rate Fast And Easy Ecgs Shade Wesley



Basic Arrhythmias C 11 American Heart Association Do Not Edit Ppt Download



Approach To Ecg Interpretation Springerlink



Http Samples Jbpub Com Ch04 Pass02 Levine Pdf



Rate Ecgpedia




Cv Physiology Determining Heart Rate From The Electrocardiogram



Shadechapter03 Ppt Read Only



Nursing Bibs Ekg Rate




Heart Rate The Premier Ekg Resource For Medical Professionals Ekg Md Dr Anthony Kashou




Ecg Basics Rebel Em Emergency Medicine Blog
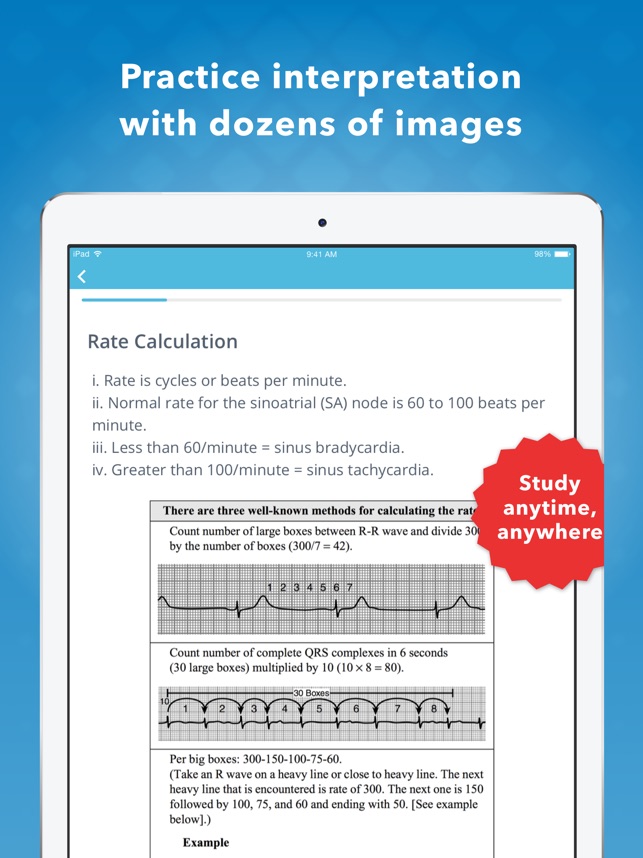



Ecg Ekg Mastery On The App Store




Heart Rate The Premier Ekg Resource For Medical Professionals Ekg Md Dr Anthony Kashou




Ecg Basics Rebel Em Emergency Medicine Blog
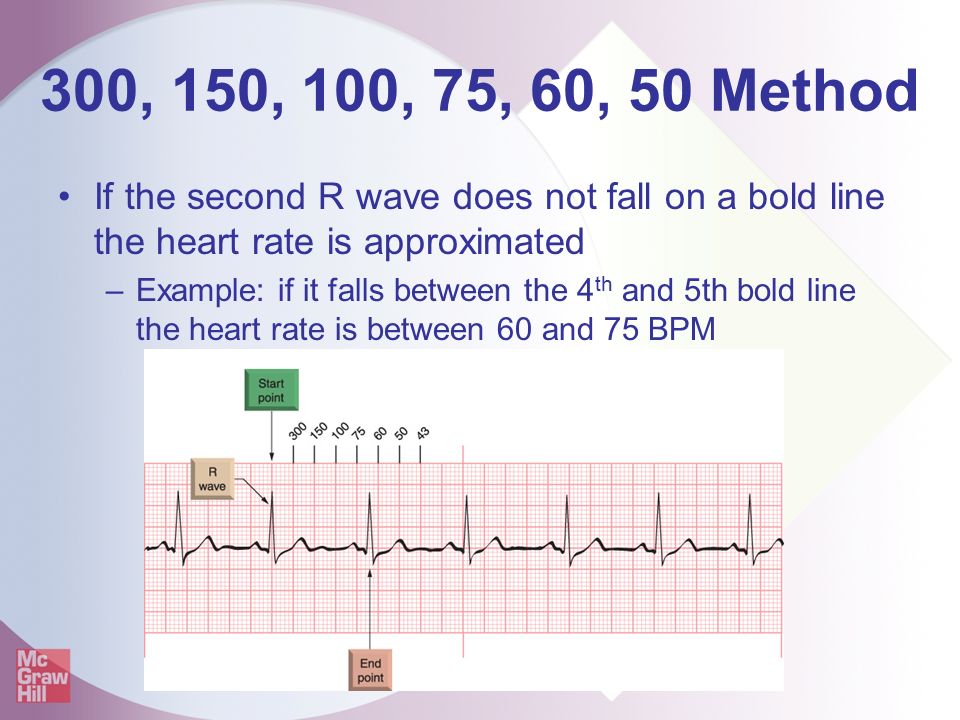



Fast Easy Ecgs A Self Paced Learning Program Ppt Video Online Download



Ecg A Pictorial Primer




Ekg Interpretation




Patwari Academy Ecg Rate Rhythm Axis



Ecg Tips




Ecg Interpretations How To Analyze A Rhythm Normal Sinus Rhythm Heart Arrhythmias Diagnosing A Myocardial Infarction Online Presentation




3 Heart Rate Fast Easy Ecgs A Selfpaced
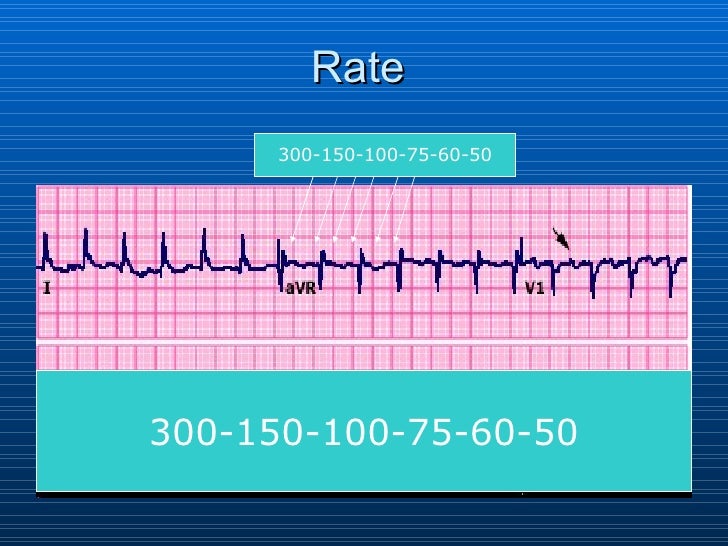



Ecg Interpretation



Www oms Org Docs Handouts rc Ekg Lecture Primer Pdf



Chapter 1 For 12 Lead Training Rhythm Basics Ppt Video Online Download



Ecg Rate Interpretation Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Basics




Heart Rate And Rhythm Springer Publishing



What Do Normal And Abnormal Heart Rhythms Look Like On Apple Watch By Brandon Ballinger Cardiogram




Determining Rate Learn The Heart



Triplets R To R 6 Second Heart Rate Method



Electrocardiography Basic Knowledge With Focus On Fetal And Pediatric Ecg Springerlink



Ekg Paper Ems Education




Ch 5 Calculating Heart Rate Flashcards Quizlet




Ecg Basics Rebel Em Emergency Medicine Blog



How Is The Heart Rate Determined On Electrocardiography Ecg



1



Large Block Method To Calculate Heart Rate Ecg Medical Training



Dr Boyd St Elizabeth Healthcare Ppt Download



How To Read An Ecg



Www Justintimemedicine Com Api Cms Media File 62 Pdf



Www Asapa Org Resource Resmgr 17 Spring Frost Ekg Review 5bcompatibil Pdf



Ecg Interpretation Manual Of Medicine



Ecg Basics Methods Of Heart Rate Calculation Youtube



Www Bannerhealth Com Media Files Project Bh Careers Reviewforekgs16aclsv51 Ashx



How To Read An Ecg



Rate Ecgpedia




Ekg Interpretation Cheat Sheet 1 Rate Regular Grepmed



Ecg A Pictorial Primer



How To Read Ecg




Ecg Basics Rebel Em Emergency Medicine Blog




Introduction To Ecgs 1 Discussion Topics N Ecg



印刷 300 150 100 75 60 50 300 150 100 75 60 50 Pngfreegejpl6d4




Using The 300 150 100 75 60 50 Method Youtube



Ecg Basics Rebel Em Emergency Medicine Blog




Ecg Basics Methods Of Heart Rate Calculation Youtube




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader



Ecg Rate Interpretation Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Basics




Ecg Interpretation Ppt Download



Ecg Part 2




Electrocardiography Lecture Notes Studocu



Ppt Heart Rate Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Ecg Basics 3 Pdf



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿